C01
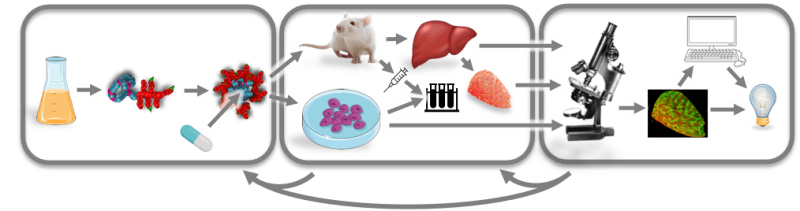
Dextran derivatives and polyesters are synthesized and used as carrier materials for inhibitors that target inflammatory pathways in hepatic stellate cells to slow down the development of liver fibrosis. Advanced biophotonic imaging is utilized to characterize the inhibitor-loaded nanoparticles in cells or directly in the liver. The nanoparticle induced modulation and activation of stellate cells are also analyzed through omics-methods. These joint efforts allow for novel approaches to therapeutically target hepatic stellate cells.
Grafik Projekt C01
Graphic: S. SchubertPrinciple investigators
Prof. Dr. Jürgen Popp
Image: Prof. Dr. Jürgen PoppProf. Dr. Jürgen Popp
Institute for Physical Chemistry (IPC)
Friedrich Schiller Unviversity of Jena
Helmholtzweg 4
07743 Jena
Phone: +49 3641 9-48320
juergen.popp@uni-jena.de
Dr. Stephanie Schubert
Image: Dr. Stephanie SchubertDr. Stephanie Schubert
Institute of Pharmacy (IP)
Friedrich Schiller University Jena
Lessingstrasse 8
07743 Jena
Phone: +49 3641 9-48599
stephanie.schubert@uni-jena.de
Prof. Dr. Michael Bauer
Image: Prof. Dr. Michael BauerProf. Dr. Michael Bauer
Center for Sepsis Control and Care (CSCC)
University Hospital Jena (UKJ)
Clinic for Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine
Am Klinikum 1
07747 Jena
Phone: +49 3641 9-323100
michael.bauer@med.uni-jena.de
Staff
Mira Behnke
Image: Mira BehnkeMira Behnke
Center for Applied Research (ZAF)
Friedrich Schiller University Jena
Philosophenweg 7
07743 Jena
Phone: +49 3641 9-48575
mira.behnke@uni-jena.de
Klea Mehmetaj
Image: Klea MehmetajKlea Mehmetaj
Center for Sepsis Control and Care (CSCC)
University Hospital Jena (UKJ)
Forschungszentrum Lobeda (FZL)
Erlanger Allee 101
07747 Jena
Klea.Mehmetaj@med.uni-jena.de
Julian Plitzko
Image: Leibniz-IPHTJulian Plitzko
Institute for Physical Chemistry (IPC)
Friedrich Schiller Unviversity of Jena
Helmholtzweg 4
07743 Jena
julian.plitzko@uni-jena.de
Franziska Adermann
Image: Mira BehnkeFranziska Adermann
Center for Applied Research (ZAF)
Friedrich Schiller University Jena
Philosophenweg 7
07743 Jena
franziska.adermann@uni-jena.de
Thorben Köhler
Image: Thorben KöhlerThorben Köhler
Center for Applied Research (ZAF)
Friedrich Schiller University Jena
Philosophenweg 7
07743 Jena
Germany
Phone: +49 3641 9-48581
Fax: +49 3641 9-48202
thorben.koehler@uni-jena.de